Learn the essential chicken breast nutrition facts that make it a key player in a healthy diet. Uncover the protein, vitamins, and minerals that make chicken breast a top choice for nourishing your body. Dive into the health benefits and get practical cooking tips for maximizing its nutritional value.
Chicken breast is a popular and versatile protein source that can be found in various cuisines around the world. It is known for its lean meat, making it an excellent choice for those looking to maintain a healthy diet.
But what exactly makes chicken breast a nutritional powerhouse? In this article, we will dive into the health secrets of chicken breast and why it should be a staple in your diet.

Key Nutritional Components
A. Protein Content
1. Role of Protein in Muscle Building and Repair
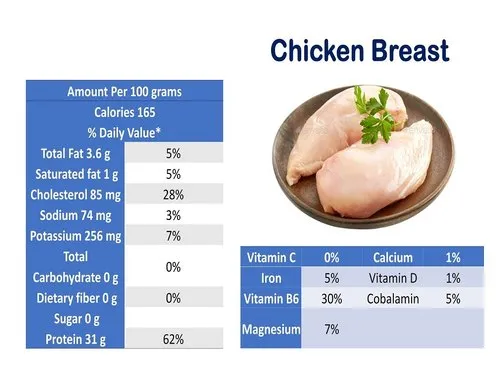
Chicken is a rich source of high-quality protein, which plays a crucial role in muscle building, repair, and maintenance. Protein is composed of amino acids, which are the building blocks of muscles. Therefore, consuming chicken breast can help support muscle growth and repair.
2. Recommended Daily Intake of Protein
Protein intake requirements vary based on age, gender, and activity level; however, in general, it is recommended to consume 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. This means that a 150-pound person would need approximately 54 grams of protein per day, and a 200-pound person would require around 72 grams of protein daily.
3. Comparing Chicken Breast to Other Protein Sources
Chicken breast is considered one of the best sources of lean protein, as it contains all essential amino acids in adequate amounts. Other sources of protein, such as red meat and dairy products, may contain high levels of saturated fat, making chicken breast a healthier alternative.
B. Essential Nutrients
1. Vitamins
Chicken is packed with B vitamins, which are essential for a wide range of bodily functions, including energy production and brain function. It is also a good source of vitamin A, which supports healthy vision and immune function.
2. Minerals
In addition to vitamins, chicken breast contains an array of essential minerals such as iron, zinc, and selenium. These minerals play crucial roles in maintaining healthy bones, promoting wound healing, and supporting the immune system.
C. Low in Calories and Fat
1. Benefits for Weight Management
With its low calorie and fat content, chicken breast can be an excellent choice for those looking to manage their weight. A 3-ounce serving of skinless, boneless chicken breast contains only 140 calories and 3 grams of fat, making it a filling yet healthy option.
2. Saturated Fat Content
Saturated fat is known to increase levels of bad cholesterol in the body, which can lead to an increased risk of heart disease. Chicken breast is naturally low in saturated fat, with only 1 gram per 3-ounce serving.
Micronutrients in Chicken Breast
Chicken breast, apart from being a powerhouse of protein, vitamins, and minerals, also contains valuable micronutrients that contribute to its nutritional profile. Micronutrients, though required in smaller quantities than macronutrients, are essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing disease.
A. Iron
Iron is a micronutrient present in chicken breast that aids in the production of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to all parts of the body. A diet rich in iron can help prevent iron-deficiency anemia.
B. Zinc
Zinc, another micronutrient found in chicken breast, supports the immune system and aids in wound healing. It also plays a critical role in DNA synthesis and cell division.
C. Selenium
Chicken breast is a good source of selenium, a micronutrient that acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage. Selenium also helps support a healthy metabolism.
D. Copper
Though required in very small amounts, copper is a vital micronutrient that assists in the production of red and white blood cells and triggers the release of iron to form hemoglobin. Copper is also important for maintaining healthy bones and nerves.
E. Phosphorus
Chicken breast is also a valuable source of phosphorus, a micronutrient that plays a pivotal role in maintaining strong and healthy bones. Phosphorus works in tandem with calcium to form the mineral matrix of the bones, promoting optimal bone density. An adequate intake of phosphorus can therefore contribute significantly to bone health and the prevention of conditions such as osteoporosis.
F. Niacin (Vitamin B3)
Niacin, also known as Vitamin B3, is another micronutrient abundant in chicken breast. It plays an integral role in conversion of nutrients to energy, supporting the metabolism process within the body. Niacin aids in the functionality of the digestive system, nervous system, and skin health. A diet rich in niacin can help maintain good health and metabolic efficiency.
Health Benefits of Chicken Breast
Consumption of chicken breast has numerous health benefits due to its rich nutritional profile. Here are some of the key benefits:
A. Support for Weight Loss
Chicken breast, with its high protein content and low levels of fat and calories, plays a crucial role in weight management. High protein foods like chicken breast can increase feelings of satiety and reduce overall calorie intake, facilitating weight loss.
B. Muscle Health and Development
The high-quality, lean protein found in chicken breast promotes muscle growth and aids in muscle repair after intense exercise. Consuming chicken breast after a workout can help optimize muscle recovery and development.
C. Cardiovascular Health
Chicken breast is a heart-healthy food. It’s low in saturated fat, which helps maintain healthy cholesterol levels and reduces the risk of heart disease. Moreover, the presence of essential nutrients like niacin and vitamins B6 and B12 contribute to a healthy cardiovascular system.
Cooking Tips for Maximum Nutrient Retention

A. Grilling vs. Baking
Choosing the right cooking method can significantly affect the nutrient retention in chicken breast. Both grilling and baking are excellent choices as they require less oil, hence preserving the original nutritional value of the chicken. Grilling imparts a smoky flavor and can reduce the overall fat content as excess fat drips off the grates.
However, it’s important to avoid charring the meat, as it can lead to the formation of harmful compounds. On the other hand, baking is a gentler cooking method that minimizes nutrient loss. It’s ideal for retaining the moisture and tenderness of the chicken breast, thus preserving its inherent flavor and nutrients.
B. Marinating for Enhanced Flavor without Sacrificing Nutrition
Marinating chicken breast not only enhances its flavor but can also help to retain its nutritional profile. Using healthy ingredients like olive oil, lemon juice, herbs, and spices for your marinade adds minimal extra calories while significantly boosting flavor.
Acidic ingredients in marinades, such as lemon juice or vinegar, can help to tenderize the meat, while herbs and spices add a wealth of flavors without increasing the calorie content. Moreover, marinating can also reduce the formation of harmful compounds during cooking, making your chicken breast meal healthier and more flavorful.
WHEN SHOULD YOU EAT FAST FOOD? : “EAT SMART AND IMPROVE YOUR HEALTH AND WELL-BEING -Read it
Common Misconceptions About Chicken Breast and Nutrition
There are several misconceptions surrounding breast and its nutritional value. Some people wrongly believe that chicken breast is devoid of any real nutritional value and consists only of protein. This is far from the truth.
As mentioned earlier, breast is not only a high-quality protein source but also a rich reservoir of vital vitamins, minerals, and micronutrients essential for maintaining optimal health.
Addressing Concerns Related to Cholesterol and Health Risks
A common concern pertaining to the consumption of chicken breast revolves around its cholesterol content. Many people believe that eating chicken breast will lead to high cholesterol levels and subsequent heart-related issues. However, it is important to note that chicken breast, particularly skinless, is low in saturated fat, the primary dietary cause of high cholesterol.
Furthermore, it is abundant in heart-friendly nutrients such as niacin, and vitamins B6 and B12, making it a healthy choice for those mindful of cardiovascular health. It is, however, important to prepare it in a healthy way – grilling, baking, or using a healthy marinade – to ensure that its nutritional properties are preserved.
Chicken Breast Quality and Sourcing
When it comes to consuming chicken breast, the quality of your source can greatly impact both the taste and the nutritional value of the meat. Here are a few factors to consider:
A. Importance of Choosing High-Quality Chicken
The quality of the breast you choose can significantly influence its nutritional profile and the overall health benefits that you can derive from it. High-quality chicken, usually sourced from chickens that are raised in good conditions and fed a healthy diet, tend to be richer in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals.
Moreover, high-quality breast is often free from antibiotics, growth hormones, and other potentially harmful substances that can be found in lower quality alternatives.
B. Organic and Free-Range Options
Organic and free-range chickens are excellent options for high-quality chicken breast. Organic chickens are raised without the use of antibiotics or hormones and are fed an organic diet, free from pesticides and artificial ingredients.
This can lead to a more nutritious and flavorful meat. Free-range chickens, on the other hand, have the freedom to roam outdoors, leading to a more diverse diet and more exercise, which can positively impact the nutritional profile and texture of the meat. Although these options may cost a bit more, the quality of the meat and the health benefits they offer make them a worthwhile investment.
Sample Recipes
A. Healthy Chicken Breast Recipes with Nutritional Breakdowns
- Grilled Lemon Herb Chicken Breast
- Ingredients: 1 lb chicken breast, juice of 1 lemon, 2 tablespoons olive oil, 2 cloves garlic (minced), 1 tablespoon fresh rosemary (finely chopped), salt, and pepper to taste.Directions: Marinate the chicken in the lemon juice, olive oil, garlic, rosemary, salt, and pepper for at least 2 hours. Preheat grill and cook chicken for about 6-8 minutes on each side until done.Nutritional breakdown (per serving): Calories: 165, Protein: 26g, Fat: 6g, Carbs: 1g
- Baked Chicken Breast with Quinoa and Steamed Vegetables
- Ingredients: 1 lb chicken breast, 1 cup quinoa, 2 cups mixed vegetables (e.g., broccoli, bell peppers, zucchini), 2 tablespoons olive oil, salt, and pepper to taste.Directions: Preheat oven to 375°F (190°C), season chicken with salt and pepper, and bake for 25-30 minutes or until done. Cook quinoa according to package instructions. Steam vegetables until tender. Serve the chicken with quinoa and vegetables.Nutritional breakdown (per serving): Calories: 240, Protein: 28g, Fat: 10g, Carbs: 20g
- Salads: Adding grilled or baked breast to salads not only adds to the protein content but also makes the salad more filling. Opt for a variety of colorful vegetables and a light dressing to keep it fresh and healthy.Wraps: Use whole grain tortillas, lean chicken breast, and plenty of vegetables to create a nutritious and balanced meal. Add some Greek yogurt or hummus for added flavor without the extra calories.Soups and stews: Chicken breast can be a great addition to soups and stews. It provides a lean protein source and absorbs the flavors of your soup or stew beautifully.As a topping for whole grain pizza: Thinly sliced chicken breast can be a healthier alternative to traditional high-fat pizza meats. Pair it with lots of vegetables and a thin whole grain crust for a balanced meal.
Chicken Breast Nutrition Facts conclusion-
chicken is a highly versatile and nutritious food. Contrary to prevalent misconceptions, it is not just a source of high-quality protein but also a treasure trove of vital vitamins, minerals, and micronutrients. Chicken breast, especially skinless, is low in saturated fat, making it a heart-friendly choice.
The quality of breast, whether it is organic, free-range, or conventional, greatly influences its nutritional profile, with higher-quality options often containing more beneficial omega-3 fatty acids and fewer potentially harmful additives.
Making informed food choices is a key component of a healthier lifestyle. Choosing high-quality chicken and preparing it in ways that preserve its nutritional properties can significantly contribute to your overall health and wellbeing.
Incorporating chicken breast into your diet in diverse and interesting ways, such as in salads, wraps, soups, or even as a topping on a whole grain pizza, can make your meals both nutritious and enjoyable.
However, remember that a balanced diet involves variety. Alongside chicken , be sure to consume a wide array of other protein sources, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Here’s to a healthier and more informed approach to eating!
For further reading and a deeper understanding of the information presented above, please refer to the following reputable sources and scientific studies:
- The Nutritional Value of Chicken: This article from the National Institutes of Health provides a comprehensive overview of the nutritional value of chicken.
- Organic Poultry and Eggs Capture High Price Premiums and Growing Share of Specialty Markets: This report from the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) offers a detailed look at the organic poultry market, including the benefits of organic chicken.
- The effects of outdoor access on the welfare of broilers: This study published in the Poultry Science journal investigates the impact of free-range systems on the wellbeing of chickens.
- Chicken consumption and the risk of prostate cancer: a meta-analysis: This meta-analysis found on PubMed looks at the potential health implications of chicken consumption.
- Dietary protein and muscle mass: Translating science to application and health benefit: This article from the National Institutes of Health discusses how protein – such as that found in chicken – can aid muscle mass.
- The US Dietary Guidelines: For a comprehensive understanding of a balanced diet, these guidelines from the US Department of Health and Human Services provide helpful information.
Remember to always consult with a healthcare provider or a nutrition expert when making significant changes to your diet.
Proudly powered by Ultimate Blog Hub


Pingback: High-Protein Frozen Meals: Convenient & Nutritious Options
Pingback: Thai BBQ: Exploring Flavors with the Best BBQ Tool Set